Thoroughbred Sales Assessment; Update from the Gerald Leigh Memorial Lectures, 2019
/By Tom O’Keeffe
The Beaufort Cottage Educational Trust Gerald Leigh Memorial Lectures took place this year at the National Horseracing Museum in Newmarket and a host of international and local veterinary specialists and industry leaders were present to discuss the veterinary aspects of the sales selection of the thoroughbred.
Gerald Leigh was a prominent breeder and racehorse owner until his death in 2002; and his friend and vet Nick Wingfield Digby opened the seminar and introduced the speakers. The Gerald Leigh Charitable Trust has established this annual lecture series to provide a platform for veterinary topics relating to the thoroughbred to be discussed amongst vets and prominent members of the industry.
Sir Mark Prescott described his take on the sales process and some of the changes he has noted since his early involvement in the industry. He recalled how the first Horses in Training sale he attended had only 186 horses. In those early days, his role was to sneak around the sales ground stables late at night on the lookout for crib biters. Back then, there was no option to return horses after sale, and as a result, trainers preferred to buy horses from studs they were familiar with—a policy Sir Mark still follows to this day.
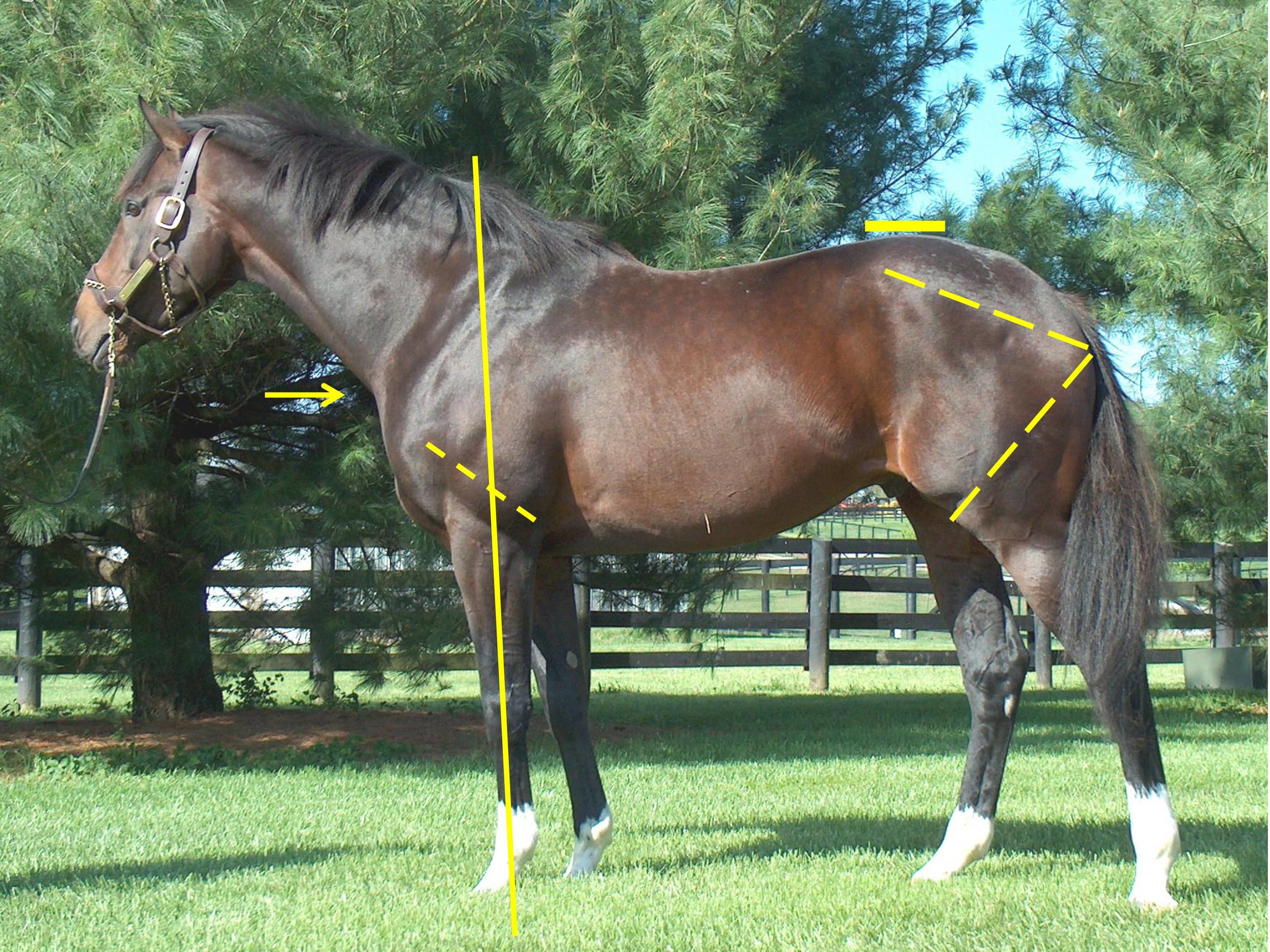
Sir Mark went on to explain that he believes strongly that the manner in which an animal is reared has a strong bearing on their ability to perform at a later date. Sir Mark also mentioned that horses can cope with many conformational faults nowadays that would have been deemed unacceptable in his early years. He attributed this to improvements in ground conditions, such as watering and all-weather surfaces. Mike Shepherd, MRCVS, of Rossdales Equine Practice in Newmarket had been tasked with describing and discussing the sales examination from a veterinary viewpoint and in particular attempting to define what vets are trying to achieve in this process.
Shepherd’s key message was that the physical exam is the cornerstone of any veterinary evaluation. A vet examining a horse on the sales ground is not a guarantee that the horse will never have an issue—there is no crystal ball. Owners and trainers should be aware there are several limitations of the vetting process, and it is helpful to think in terms of a “pre-bid inspection” rather than a “pre-purchase examination”. The horse is away from its home environment, and this puts a lot of stress on the animal. In most cases, pre-purchase exercise is not possible, so conditions that are only apparent when the horse is exercising and in training may go undetected.
Time is a major challenge, with both vendors and prospective purchasers pushing for everything to be done as quickly as possible. A busy sales vet may have a long list of horses to examine, and information on each must be transferred to their client coherently and clearly—all before the horse is presented for sale. It can be challenging to acquire a detailed veterinary history. Previous surgeries, medication and vices displayed by the animal ought to be reported, but in many cases the person with the horse is not in a position to accurately answer questions on longer-term history.
Everyone involved—the vendor, the prospective purchaser, and the auction house—wants the process to go ahead. The horse to be bought/sold and the vet can be seen as a stumbling block. Prospective purchasers may want the horse to be examined clinically, its laryngeal function examined by endoscope, radiographs of the horse’s limbs either reviewed or taken, ultrasound examinations of their soft tissue structures and heart performed. The role of the vet is to help the purchaser evaluate all this information and make an evidence-based decision on whether to purchase the horse.
Examining vets can face conflicts of interest when examining horses that are under the ownership or care of one of their clients. Shepherd explained how Rossdales, and some other practices involved in sales work, have a protocol that an examining vet will not perform a vetting on a horse in the care of one of their own clients, and will disclose to the prospective purchaser if the vendor is a client of the practice. It is crucial to avoid working for both buyer and seller as a conflict of interest becomes unavoidable.
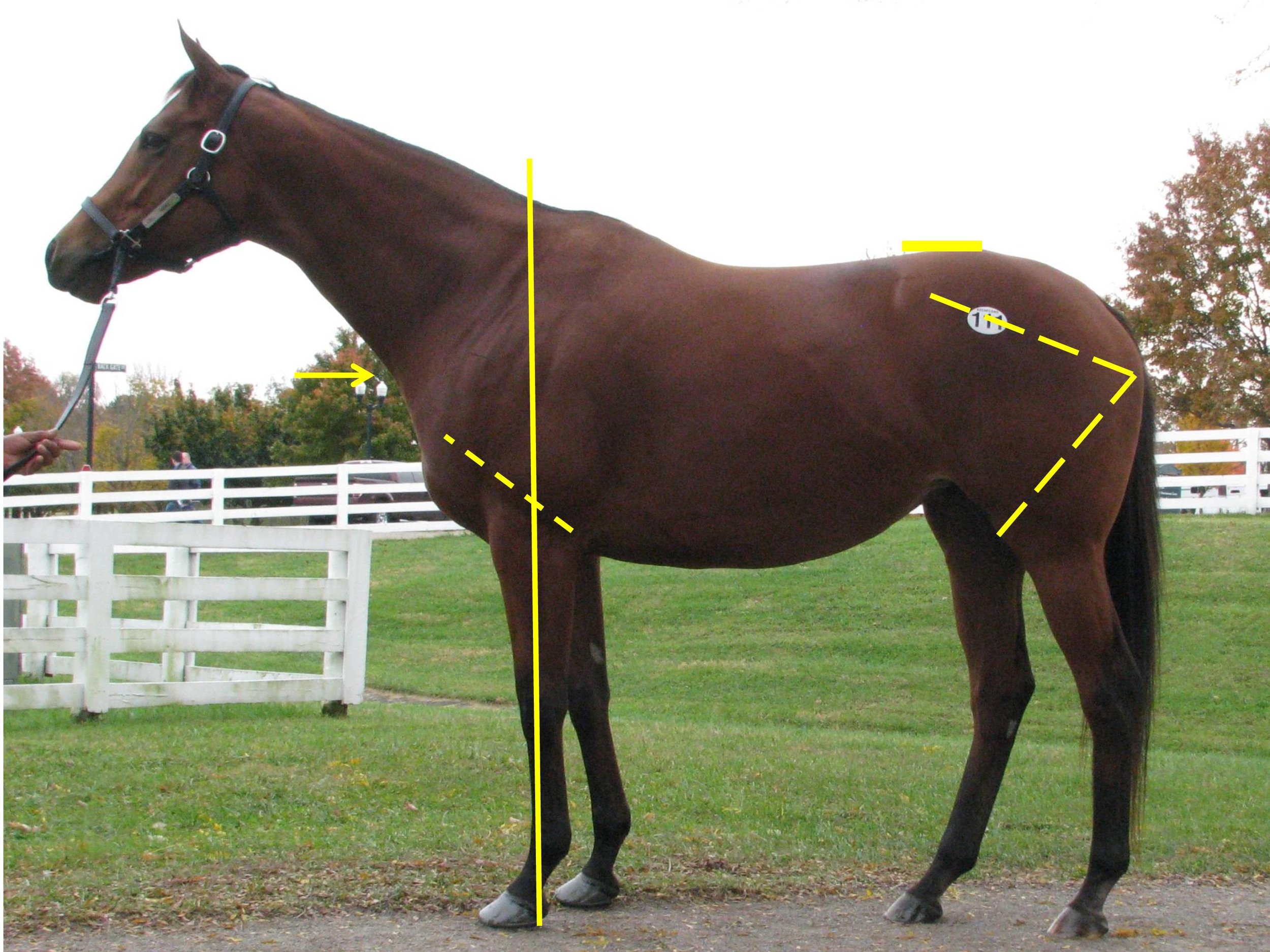
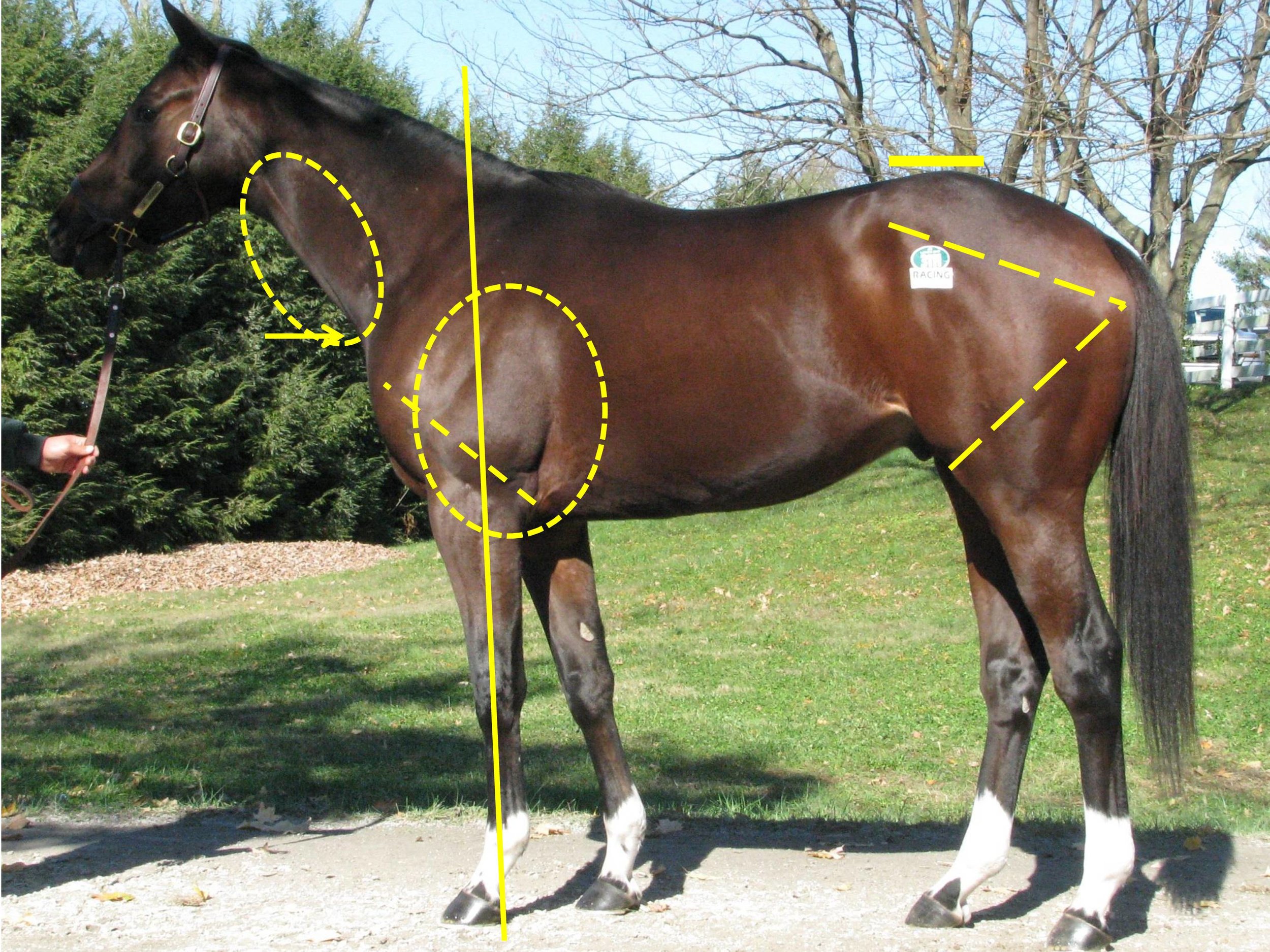
It is also essential that the vet understands exactly what the horse is expected to do following the sale. Thoroughbred horses in flat racing have short timescale targets and, as a result, certain parts of the examination carry more weight than others. For example, the knees and fetlock joints are commonly implicated in lameness in flat racehorses; thus particular attention must be paid to these joints when examining yearlings. Soft tissue injuries are impactful in all young thoroughbreds, but there is a particular emphasis on tendon integrity in the National Hunt racehorse because career-threatening tendon injuries are particularly prevalent in these horses. When evaluating potential broodmares, good feet are very relevant, and overall conformation is particularly important if the aim is to breed to sell. Vetting horses for clients aiming to pin hook their purchases places different requirements on the examining vet. These horses need to be able to cope with the preparation required for another sale, and they must also stand up to the scrutiny of vets at a later sale. The horse’s walk and conformation rank high in the foal/ yearling stage but may be judged to be less significant if the horse breezes in a fast time at a breeze up sale.
It is also critical that purchasers recognise that many of the common veterinary issues encountered in training are not detectable at the Sales stage. …