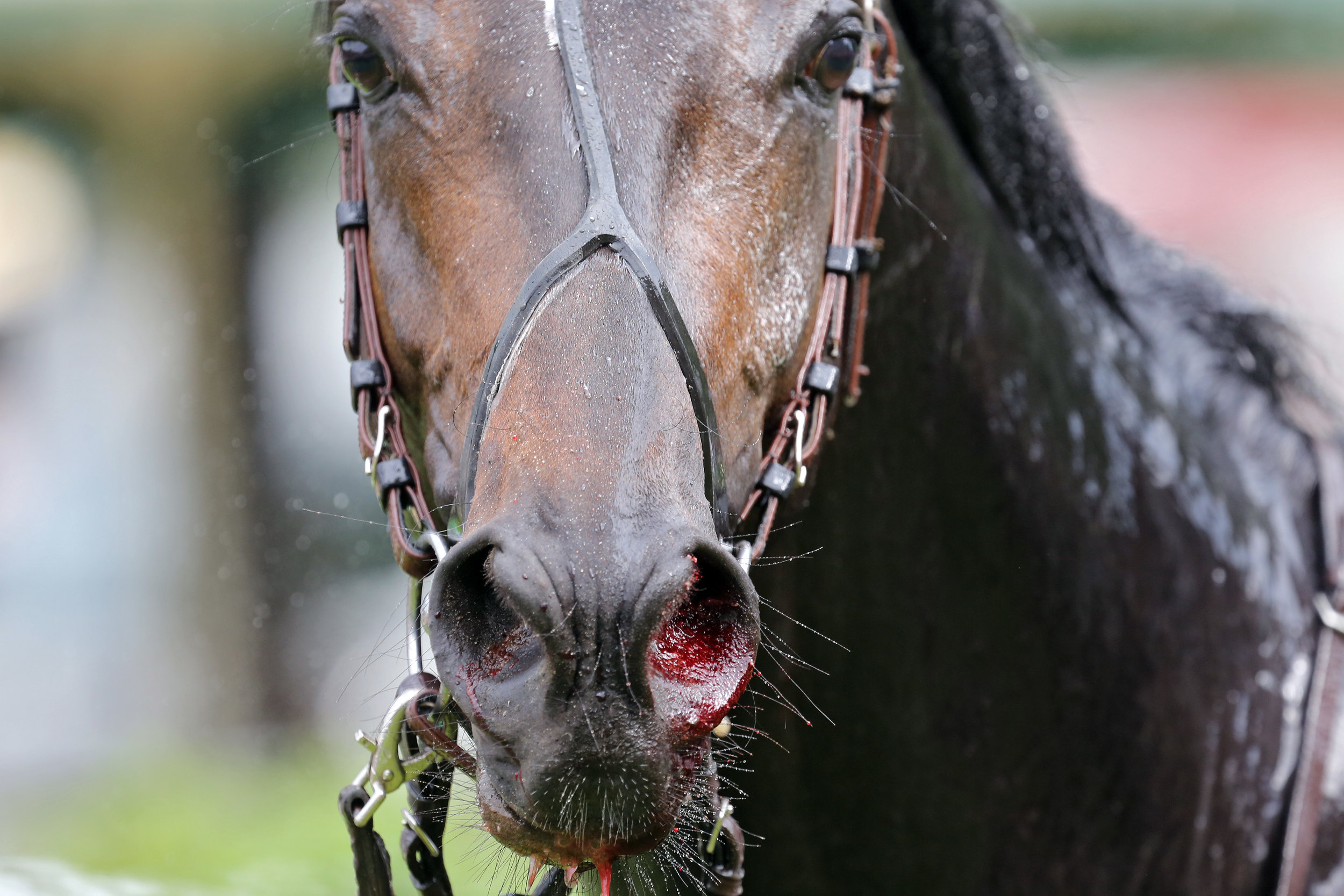
EIPH: An Australian Perspective with Worldwide Implications
/By Ellie Crispe and Guy Lester
Exercise-induced pulmonary haemorrhage (EIPH) is a common disease of racehorses. The precise cause of EIPH is yet to be fully determined, but a well-accepted theory is that lung blood vessels rupture in response to the extremely high blood pressure and low airway pressure experienced during strenuous exercise. The barrier that separates the airway from the blood vessels is ultra-thin to facilitate the efficient exchange of gases, but this predisposes to breakage. The condition is most frequently described in Thoroughbred and Standardbred racehorses, but it has also been identified in racing Appaloosas and Quarter Horses, as well as horses involved in other high intensity athletic activities, including showjumpers, 3-day eventers, barrel racers, steeplechasers and polo horses.
EIPH is not unique to horses and has been reported in human athletes, as well as racing greyhounds and camels. Our group at Murdoch University in Perth Australia has had an interest in EIPH, which has led to three recent publications in the Equine Veterinary Journal.1-3
How common is EIPH?
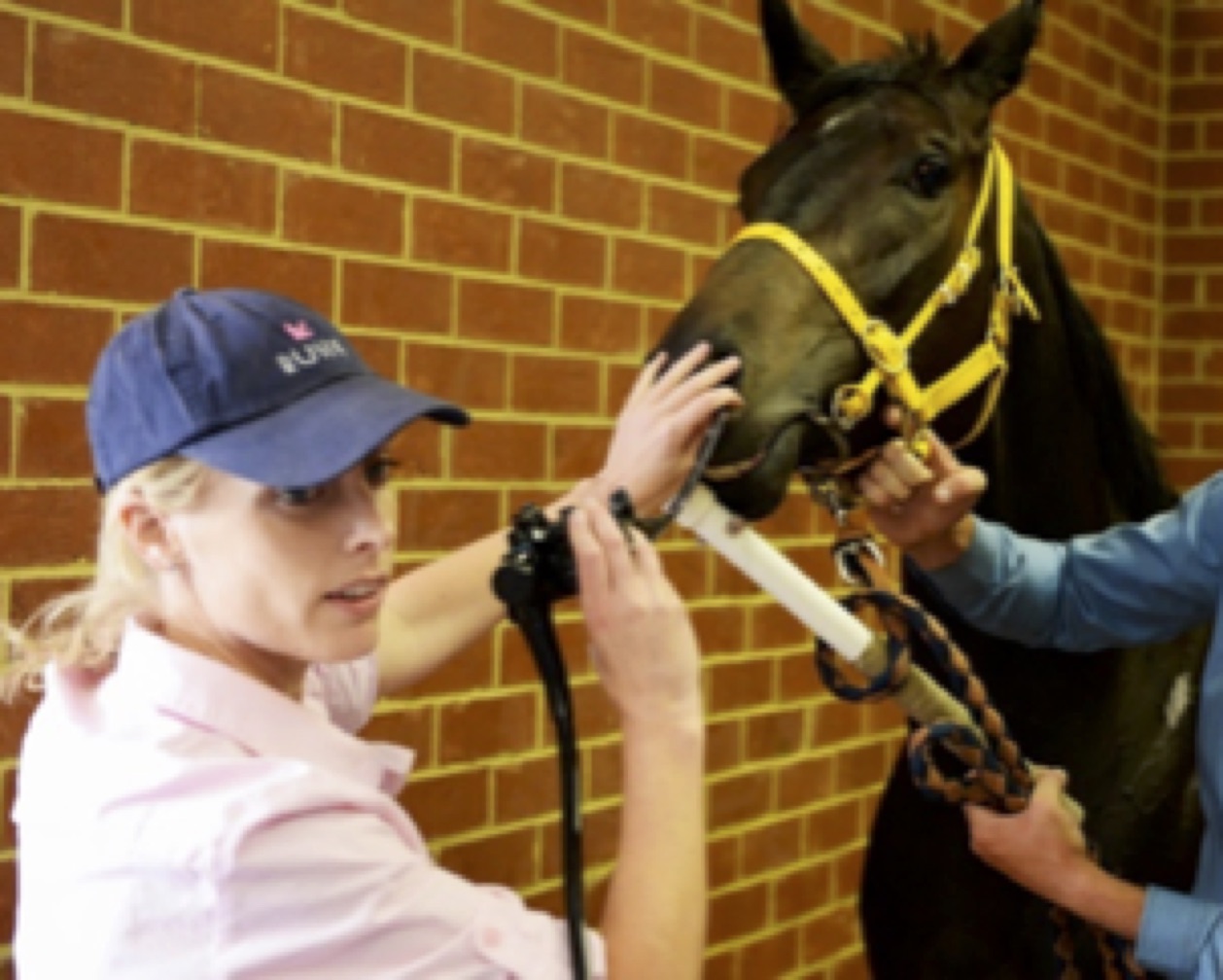
Blood from both nostrils—also known as epistaxis—is the most obvious manifestation of EIPH and occurs between 1.5 and 8.4/1000 race starts, varying with racing jurisdiction. Epistaxis represents a severe manifestation of EIPH, and basing surveys on its presence vastly underestimates the true prevalence of lung haemorrhage. There are several techniques used to diagnose EIPH, but endoscopy of the trachea 30-120 minutes after racing or galloping is a common and reliable method. Occurrence and severity of pulmonary haemorrhage is typically graded using a 0-4 scale. Using endoscopy, we reported a prevalence of EIPH post-race in Australian thoroughbreds racing on turf tracks of around 55%, with most positive horses having low to moderate volumes of blood in the trachea. EIPH is less common if horses are examined after trialling, and reduced further if examined after track gallops. The prevalence of EIPH increases when horses are examined on multiple occasions after racing, and in fact all horses in our research population that had seven monitored race-starts experienced EIPH on at least one occasion.
What is the effect of EIPH on race-day performance?
It is generally considered that EIPH has a negative impact on racing performance, but evidence for this assertion is surprisingly lacking. We performed 3,794 post-race endoscopy exams on over 1,500 Australian horses and reported that inferior race-day performance was limited to horses with severe EIPH (grades 3 and 4); this reflected only 6.3% of all examinations. Horses with the highest grades of EIPH (grade 4) were less likely to finish in the first three, finished further from the winner, were less likely to collect race earnings, were slower over the final stages of the race, and were more likely to be overtaken by other competitors in the home straight than horses without EIPH. Interestingly, horses with EIPH grade 1 or 2 were more likely to overtake others in the home straight, compared to horses without EIPH (grade 0).
It is highly unlikely that low-grade EIPH (grade 1 or 2) confers an athletic advantage; a plausible explanation is that horses that are ridden competitively to the finish are functioning at their maximal physiological limit, compared to horses that are eased up, and overtaken, during the finishing stages of the race because they are not in prize contention or are affected by interference in the home straight. Another interesting finding was that horses with moderate to severe EIPH (grades 3 or 4) raced the early and mid-sections of the race faster than horses without EIPH. It is possible that these horses reach the breaking threshold of the small lung blood vessels at an earlier stage in the race compared to horses that start the race slower, compounding the severity thereafter. A study of barrel racing horses reported that horses with the most severe grade of EIPH were faster than horses without EIPH, a finding which may also reflect this rapid acceleration increasing the risk of EIPH. It may be wise for trainers to instruct jockeys riding horses with a history of moderate to severe EIPH to refrain from racing in this manner.
What is the effect of a one-off diagnosis of EIPH over a horse’s career?…